When Cities Begin to Breathe Electricity
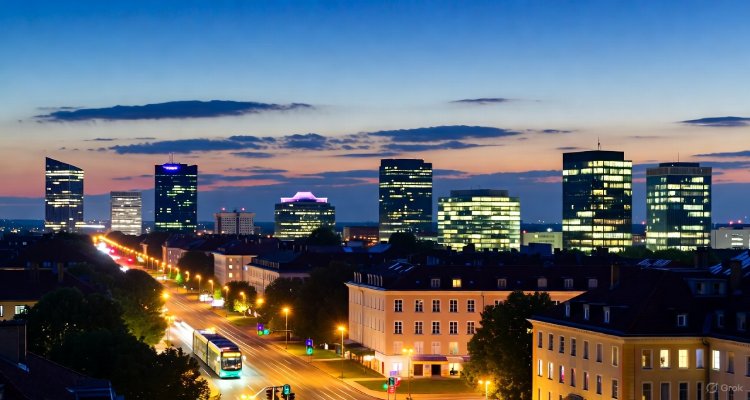

Cities worldwide are transforming with electrified infrastructure—discover how “Electricity 4.0” is reshaping urban life, resilience, and sustainability in this in-depth report.
Introduction: A New Urban Pulse
Late at night, as city lights blink to life and electric buses glide silently past, an invisible transformation pulses beneath the streets and within the walls. Around the globe, urban centers are not only illuminated by electricity but also running on it—breathing in a new rhythm as they adapt to unprecedented challenges and opportunities. From resilient high-rises powered by rooftop solar to massive data centers humming at the city’s edge, this electrification wave promises to redefine what it means for a city to be truly “alive.”infrastructurenews
Context & Background: From Power Grids to City Ecosystems
The electrification of cities is not a new idea—public electrical supply dates back to the late 19th century, when the glow of streetlights and electric trams transformed urban life forever. By the early 20th century, most large city dwellers were familiar with electric lighting, even if full electrification remained uneven. Today, the scope has dramatically widened: cities face explosive demand for digital connectivity, sustainable transport, and improved living conditions, all while contending with extreme weather, pollution, and resource scarcity.timelines.issarice+2
Across regions such as Australia, New Zealand, and major Indian cities like Delhi, the challenge is clear. Soaring electricity requirements from rising population, industry, and digital economies are stretching grids thin. Yet, there’s hope: innovative approaches like “Electricity 4.0,” which blend advanced electrification with digital control and analytics, are turning cities into smarter, more resilient ecosystems.infrastructurenews
Main Developments: Electricity 4.0 and The Urban Transformation
The latest developments in urban electrification are anchored in two key trends: widespread adoption of renewable energy and deep integration of digital technologies. Electricity 4.0 is the term used for this fusion, where everything from building management to public transport runs on an intelligent, adaptive electrical backbone.infrastructurenews
-
Smart Buildings and Grids: Buildings are now the front line of change, making up nearly 40% of global energy consumption. Solar panels, battery storage, and AI-driven energy management let buildings generate, store, and distribute power efficiently—sometimes forming microgrids that support entire neighborhoods during outages.infrastructurenews
-
Urban Mobility: Electrified public transit—buses, trams, subways—reduces air pollution and fossil fuel dependence, transforming commutes in cities like Delhi, New York, and Auckland.sciencedirect+1
-
Data Centers and Digital Economy: As cities digitize, secure and resilient power becomes crucial for data centers powering e-commerce, communications, and AI.
The payback for these investments is often rapid: many cities recoup infrastructure costs in just three to five years, thanks to lower emissions, energy savings, and enhanced public health.infrastructurenews
Expert Insight & Public Reaction
Industry experts and analysts highlight the urgency and promise of these shifts. “Investing in electrified, digital infrastructure is more than a sustainability strategy—it’s the blueprint for urban resilience,” says an urban resilience analyst from the Asia-Pacific region. Residents in innovative cities are taking notice:infrastructurenews
-
“We used to have regular blackouts and poor air quality, but it’s improved a lot since solar and smart meters came in,” reports a resident in New Delhi’s Dwarka district, where distributed solar panels now power much of the neighborhood.sciencedirect
-
Yet, progress is uneven. Technical shortcomings in grid management sometimes lead to data outages or unreliable air quality reporting, exposing the need for robust governance and real-time monitoring to protect public health.timesofindia.indiatimes
The public response is generally supportive but cautious—embracing clean, reliable power but demanding accountability and equitable access.
Impact & Implications: Who Breathes Easier?
As urban electrification ramps up, its impact ripples far beyond city limits:
-
Social Equity: The transition allows lower-income households—often reliant on biomass or kerosene—to plug into modern, safer energy, improving health and opportunities.sciencedirect
-
Climate Action: Electrified cities lower their carbon emissions dramatically, serving as global models for sustainable urbanization.infrastructurenews
-
Economic Resilience: Smarter infrastructure reduces downtime from power failures, boosts productivity, and attracts investment in tech-enabled services.
However, as with all major transitions, pitfalls remain. Without vigilant maintenance and inclusive policies, vulnerable groups risk being left behind or exposed to new forms of digital exclusion.timesofindia.indiatimes
Conclusion: The Future of Living Cities
Cities are entering a new era where they not only use electricity—they breathe it, adapt with it, and build their futures upon it. As “Electricity 4.0” transforms the very blueprint of urban existence, each step must be guided by innovation, equity, and a relentless commitment to resilience.sciencedirect+1
From the hum of electrified buses to the silent flow of energy through smart buildings, the next generation of cities is not just powered by electricity—it thrives on it, carrying us all toward a brighter, cleaner tomorrow.
Disclaimer: This article is intended for informational purposes only. All facts and expert opinions are based on publicly available research as of October 2025 and do not constitute investment, regulatory, or engineering advice.