Beyond Classrooms: XR and the New Era of Learning
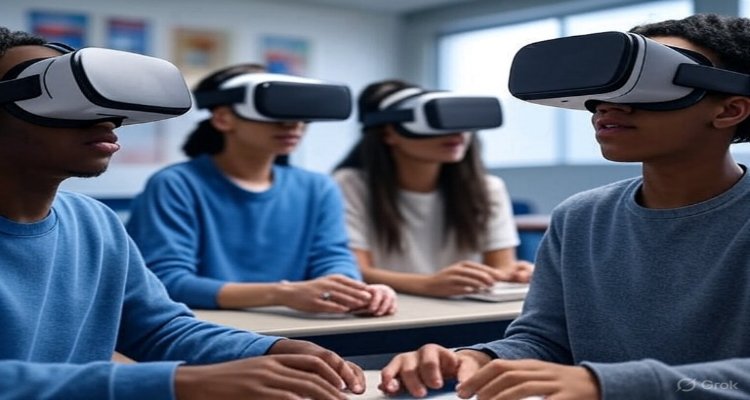

Extended Reality (XR) is reshaping education by blending immersive tech with traditional methods, creating a new era of experiential, inclusive learning.
Introduction: A New Dimension in Education
The blackboard once symbolized the heart of education. Later, projectors, computers, and tablets redefined classrooms. Today, another shift is underway—one that doesn’t just update teaching tools but fundamentally transforms how learning is experienced. Extended Reality (XR)—an umbrella term for Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (AR), and Mixed Reality (MR)—is moving education beyond classrooms, offering immersive and interactive ways to acquire knowledge.
Context & Background: From Chalk to Code
Education has always evolved alongside technology. The 20th century saw radio lessons, televised classrooms, and computer labs. In the 21st century, online learning platforms democratized access to knowledge, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic. Yet, these solutions still replicated the idea of a “screen-based classroom.” XR goes further by dissolving the boundaries between digital and physical spaces, placing learners inside three-dimensional, real-time environments where knowledge is not just read or heard but experienced.
A medical student practicing surgery in a virtual operating room, a history class walking through ancient Rome, or a language learner conversing with an AI-powered avatar—these are not distant dreams but emerging realities.
Main Developments: How XR is Entering Classrooms
Across the globe, schools, universities, and training centers are experimenting with XR to supplement—or even replace—traditional methods.
- Virtual Reality (VR): Platforms like ENGAGE and ClassVR allow students to explore virtual worlds, from the solar system to microscopic cells.
- Augmented Reality (AR): Applications like Google Expeditions and Adobe Aero overlay digital elements on real environments, enabling interactive science experiments or architectural visualizations.
- Mixed Reality (MR): Tools like Microsoft’s HoloLens blend digital objects into real-world settings, letting students manipulate complex 3D models in real time.
According to a recent report by MarketsandMarkets, the XR in education market is projected to reach $35 billion by 2030, signaling strong institutional and commercial adoption.
Expert Insight: What Educators and Analysts Say
“Extended Reality is not a gimmick—it’s a paradigm shift,” notes Dr. Angela Wu, an educational technologist at Stanford University. “Instead of passive consumption, XR fosters active participation, critical thinking, and empathy by placing learners in scenarios they can engage with.”
Educators also highlight XR’s role in inclusivity. For students with disabilities, AR-enabled content can provide tailored, accessible experiences. Meanwhile, VR can bring opportunities to remote learners who may never step into a physical lab or museum.
Public sentiment reflects both excitement and caution. While students are eager for immersive experiences, parents and policymakers raise concerns about screen time, accessibility, and equitable access across socio-economic groups.
Impact & Implications: Who Benefits and What’s Next?
The implications of XR in learning extend far beyond classrooms:
- K–12 Education: XR can turn abstract subjects like physics or chemistry into tangible, visual experiments.
- Higher Education: Universities are deploying XR for advanced simulations, from engineering prototypes to business strategy roleplays.
- Corporate Training: Companies are adopting XR for workforce upskilling, particularly in healthcare, aviation, and manufacturing, where hands-on training is critical.
- Global Learning Equity: By enabling immersive, remote education, XR has the potential to bridge gaps in underserved regions—if infrastructure challenges like internet access are addressed.
However, challenges remain. Hardware costs, content development, and teacher training are major barriers. Furthermore, ethical concerns—such as data privacy, student monitoring, and digital well-being—must be addressed to ensure responsible adoption.
Conclusion: Education Without Walls
As XR matures, education is moving from static classrooms to dynamic, borderless learning ecosystems. The shift is not about replacing teachers or traditional methods, but enhancing them with immersive, experiential tools that ignite curiosity and deepen understanding.
Just as the printing press expanded literacy and the internet expanded access, XR may well define the next educational revolution. The question is no longer whether this technology will reshape learning—but how quickly we can prepare institutions, educators, and students for this new reality.
Disclaimer : This article is for informational purposes only and does not promote any specific XR platform or product.